-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Gpu barrier memfence #3
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
base: main
Are you sure you want to change the base?
Conversation
When SPARC Asan testing is enabled by PR llvm#107405, many Linux/sparc64 tests just hang like ``` #0 0xf7ae8e90 in syscall () from /usr/lib32/libc.so.6 #1 0x701065e8 in __sanitizer::FutexWait(__sanitizer::atomic_uint32_t*, unsigned int) () at compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_linux.cpp:766 #2 0x70107c90 in Wait () at compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_mutex.cpp:35 #3 0x700f7cac in Lock () at compiler-rt/lib/asan/../sanitizer_common/sanitizer_mutex.h:196 #4 Lock () at compiler-rt/lib/asan/../sanitizer_common/sanitizer_thread_registry.h:98 llvm#5 LockThreads () at compiler-rt/lib/asan/asan_thread.cpp:489 llvm#6 0x700e9c8c in __asan::BeforeFork() () at compiler-rt/lib/asan/asan_posix.cpp:157 llvm#7 0xf7ac83f4 in ?? () from /usr/lib32/libc.so.6 Backtrace stopped: previous frame identical to this frame (corrupt stack?) ``` It turns out that this happens in tests using `internal_fork` (e.g. invoking `llvm-symbolizer`): unlike most other Linux targets, which use `clone`, Linux/sparc64 has to use `__fork` instead. While `clone` doesn't trigger `pthread_atfork` handlers, `__fork` obviously does, causing the hang. To avoid this, this patch disables `InstallAtForkHandler` and lets the ASan tests run to completion. Tested on `sparc64-unknown-linux-gnu`.
62fa928 to
a7d34b8
Compare
…110167) This is a convenient little feature of lldb, but if you didn't know it was there you'd likely never discover it.
## Problem Statement
Previously, the examples in the AST matcher reference, which gets
generated by the Doxygen comments in `ASTMatchers.h`, were untested and
best effort.
Some of the matchers had no or wrong examples of how to use the matcher.
## Solution
This patch introduces a simple DSL around Doxygen commands to enable
testing the AST matcher documentation in a way that should be relatively
easy to use.
In `ASTMatchers.h`, most matchers are documented with a Doxygen comment.
Most of these also have a code example that aims to show what the
matcher will match, given a matcher somewhere in the documentation text.
The way that the documentation is tested, is by using Doxygen's alias
feature to declare custom aliases. These aliases forward to
`<tt>text</tt>` (which is what Doxygen's `\c` does, but for multiple
words). Using the Doxygen aliases is the obvious choice, because there
are (now) four consumers:
- people reading the header/using signature help
- the Doxygen generated documentation
- the generated HTML AST matcher reference
- (new) the generated matcher tests
This patch rewrites/extends the documentation such that all matchers
have a documented example.
The new `generate_ast_matcher_doc_tests.py` script will warn on any
undocumented matchers (but not on matchers without a Doxygen comment)
and provides diagnostics and statistics about the matchers.
The current statistics emitted by the parser are:
```text
Statistics:
doxygen_blocks : 519
missing_tests : 10
skipped_objc : 42
code_snippets : 503
matches : 820
matchers : 580
tested_matchers : 574
none_type_matchers : 6
```
The tests are generated during building, and the script will only print
something if it found an issue with the specified tests (e.g., missing
tests).
## Description
DSL for generating the tests from documentation.
TLDR:
```
\header{a.h}
\endheader <- zero or more header
\code
int a = 42;
\endcode
\compile_args{-std=c++,c23-or-later} <- optional, the std flag supports std ranges and
whole languages
\matcher{expr()} <- one or more matchers in succession
\match{42} <- one or more matches in succession
\matcher{varDecl()} <- new matcher resets the context, the above
\match will not count for this new
matcher(-group)
\match{int a = 42} <- only applies to the previous matcher (not to the
previous case)
```
The above block can be repeated inside a Doxygen command for multiple
code examples for a single matcher.
The test generation script will only look for these annotations and
ignore anything else like `\c` or the sentences where these annotations
are embedded into: `The matcher \matcher{expr()} matches the number
\match{42}.`.
### Language Grammar
[] denotes an optional, and <> denotes user-input
```
compile_args j:= \compile_args{[<compile_arg>;]<compile_arg>}
matcher_tag_key ::= type
match_tag_key ::= type || std || count || sub
matcher_tags ::= [matcher_tag_key=<value>;]matcher_tag_key=<value>
match_tags ::= [match_tag_key=<value>;]match_tag_key=<value>
matcher ::= \matcher{[matcher_tags$]<matcher>}
matchers ::= [matcher] matcher
match ::= \match{[match_tags$]<match>}
matches ::= [match] match
case ::= matchers matches
cases ::= [case] case
header-block ::= \header{<name>} <code> \endheader
code-block ::= \code <code> \endcode
testcase ::= code-block [compile_args] cases
```
### Language Standard Versions
The 'std' tag and '\compile_args' support specifying a specific language
version, a whole language and all of its versions, and thresholds
(implies ranges). Multiple arguments are passed with a ',' separator.
For a language and version to execute a tested matcher, it has to match
the specified '\compile_args' for the code, and the 'std' tag for the
matcher. Predicates for the 'std' compiler flag are used with
disjunction between languages (e.g. 'c || c++') and conjunction for all
predicates specific to each language (e.g. 'c++11-or-later &&
c++23-or-earlier').
Examples:
- `c` all available versions of C
- `c++11` only C++11
- `c++11-or-later` C++11 or later
- `c++11-or-earlier` C++11 or earlier
- `c++11-or-later,c++23-or-earlier,c` all of C and C++ between 11 and
23 (inclusive)
- `c++11-23,c` same as above
### Tags
#### `type`:
**Match types** are used to select where the string that is used to
check if a node matches comes from.
Available: `code`, `name`, `typestr`, `typeofstr`. The default is
`code`.
- `code`: Forwards to `tooling::fixit::getText(...)` and should be the
preferred way to show what matches.
- `name`: Casts the match to a `NamedDecl` and returns the result of
`getNameAsString`. Useful when the matched AST node is not easy to spell
out (`code` type), e.g., namespaces or classes with many members.
- `typestr`: Returns the result of `QualType::getAsString` for the type
derived from `Type` (otherwise, if it is derived from `Decl`, recurses
with `Node->getTypeForDecl()`)
**Matcher types** are used to mark matchers as sub-matcher with 'sub' or
as deactivated using 'none'. Testing sub-matcher is not implemented.
#### `count`:
Specifying a 'count=n' on a match will result in a test that requires
that the specified match will be matched n times. Default is 1.
#### `std`:
A match allows specifying if it matches only in specific language
versions. This may be needed when the AST differs between language
versions.
#### `sub`:
The `sub` tag on a `\match` will indicate that the match is for a node
of a bound sub-matcher.
E.g., `\matcher{expr(expr().bind("inner"))}` has a sub-matcher that
binds to `inner`, which is the value for the `sub` tag of the expected
match for the sub-matcher `\match{sub=inner$...}`. Currently,
sub-matchers are not tested in any way.
### What if ...?
#### ... I want to add a matcher?
Add a Doxygen comment to the matcher with a code example, corresponding
matchers and matches, that shows what the matcher is supposed to do.
Specify the compile arguments/supported languages if required, and run
`ninja check-clang-unit` to test the documentation.
#### ... the example I wrote is wrong?
The test-failure output of the generated test file will provide
information about
- where the generated test file is located
- which line in `ASTMatcher.h` the example is from
- which matches were: found, not-(yet)-found, expected
- in case of an unexpected match: what the node looks like using the
different `type`s
- the language version and if the test ran with a windows `-target` flag
(also in failure summary)
#### ... I don't adhere to the required order of the syntax?
The script will diagnose any found issues, such as `matcher is missing
an example` with a `file:line:` prefix,
which should provide enough information about the issue.
#### ... the script diagnoses a false-positive issue with a Doxygen
comment?
It hopefully shouldn't, but if you, e.g., added some non-matcher code
and documented it with Doxygen, then the script will consider that as a
matcher documentation. As a result, the script will print that it
detected a mismatch between the actual and the expected number of
failures. If the diagnostic truly is a false-positive, change the
`expected_failure_statistics` at the top of the
`generate_ast_matcher_doc_tests.py` file.
Fixes llvm#57607
Fixes llvm#63748
… E>` should not be conditionally deleted (llvm#109363) This patch implements LWG4025: Move assignment operator of `std::expected<cv void, E>` should not be conditionally deleted. Closes llvm#105324
Achieve 100% test coverage on classes Cursor, Diagnostic, Type.
Two changes here: 1. Add significantly more detail on why this is OK, from the conversation here: https://discourse.llvm.org/t/how-to-write-an-interceptor-for-fcntl/81203 2. Change the type we expect from va_args to intptr_t, which was also a suggestion in that thread.
Summary: This was intended to be a neat optimization, but some objects come from archives so this won't work. I could write some code to detect if it came from an archive but I don't think it's wroth the complexity when this already doesn't work on Windows.
…108064) In addition to the basic mode, the ds_swizzle_b32 is supposed to support two specific modes: fft and rotate. This patch implements those two modes.
llvm#110282) When we're lowering to a split sequence, we only need one materialization of the zero constant. Our codegen looks something like this: vmv.v.i v24, 0 vmerge.vim v8, v24, -1, v0 vmv1r.v v0, v16 vmerge.vim v16, v24, -1, v0 Note: Doing this specific case since it was pointed out in llvm#110164 (comment), but it's worth noting that we have the same basic problem (over costing split operations with split invariant terms) at multiple places through this file.
The srem case of SimplifyDemandedUseBits partially duplicates KnownBits::srem. It is guarded by a statement that takes the absolute value of the RHS and checks whether it is a power of 2, but the abs() call here useless, since an srem with a negative RHS is flipped into one with a positive RHS, adjusting LHS appropriately. Stripping the abs call allows us to call KnownBits::srem instead of partially duplicating it.
…ead of #ifdef" (llvm#110310) Reverts llvm#110185 There are inconsistencies in some of these macros, which unfortunately isn't caught by a single upstream bot.
…m#108408) Simplify code by refactoring some common handling for node creation into a helper function.
This is now handled by the explicit unroller.
This reverts commit ca47f48.
Need to check if number of elements form a full register before trying per-register permutations to avoid compiler crash
Also adds additional test coverage in Analysis/ScalarEvolution/trip-count-urem.ll Extra test coverage is for llvm#108777.
There's a check here to not use aligned_alloc on macOS versions before 10.15, this patch adds an equivalent check that tests for iOS 13.
Call conversion functions directly instead of using them for type conversion on library function calls via `ctypes`' `errcheck` functionality.
…vm#91798) This allows catching OOB accesses inside `unique_ptr<T[]>` when the size of the allocation is known. The size of the allocation can be known when the unique_ptr has been created with make_unique & friends or when the type necessitates an array cookie before the allocation. This is a re-aplpication of 45a09d1 which had been reverted in f11abac due to unrelated CI failures.
…0091) This used to filter any names with `_` in them, apart from enum-constants. Resulting in discrepancies in behavior when we had fields that have `_` in the name, or for accessors like `set_`, `has_`. The logic seems to be trying to filter mangled names for nested entries, so adjusted logic to only do so for top-level decls, while still preserving some public top-level helpers. Heuristics are still leaning towards false-negatives, e.g. if a top-level entity has `_` in its name (`message Foo_Bar {}`), it'll be filtered, or an enum that prefixes its type name to constants (`enum Foo { Foo_OK }`).
Improve performance by moving the check forward to the matching stage
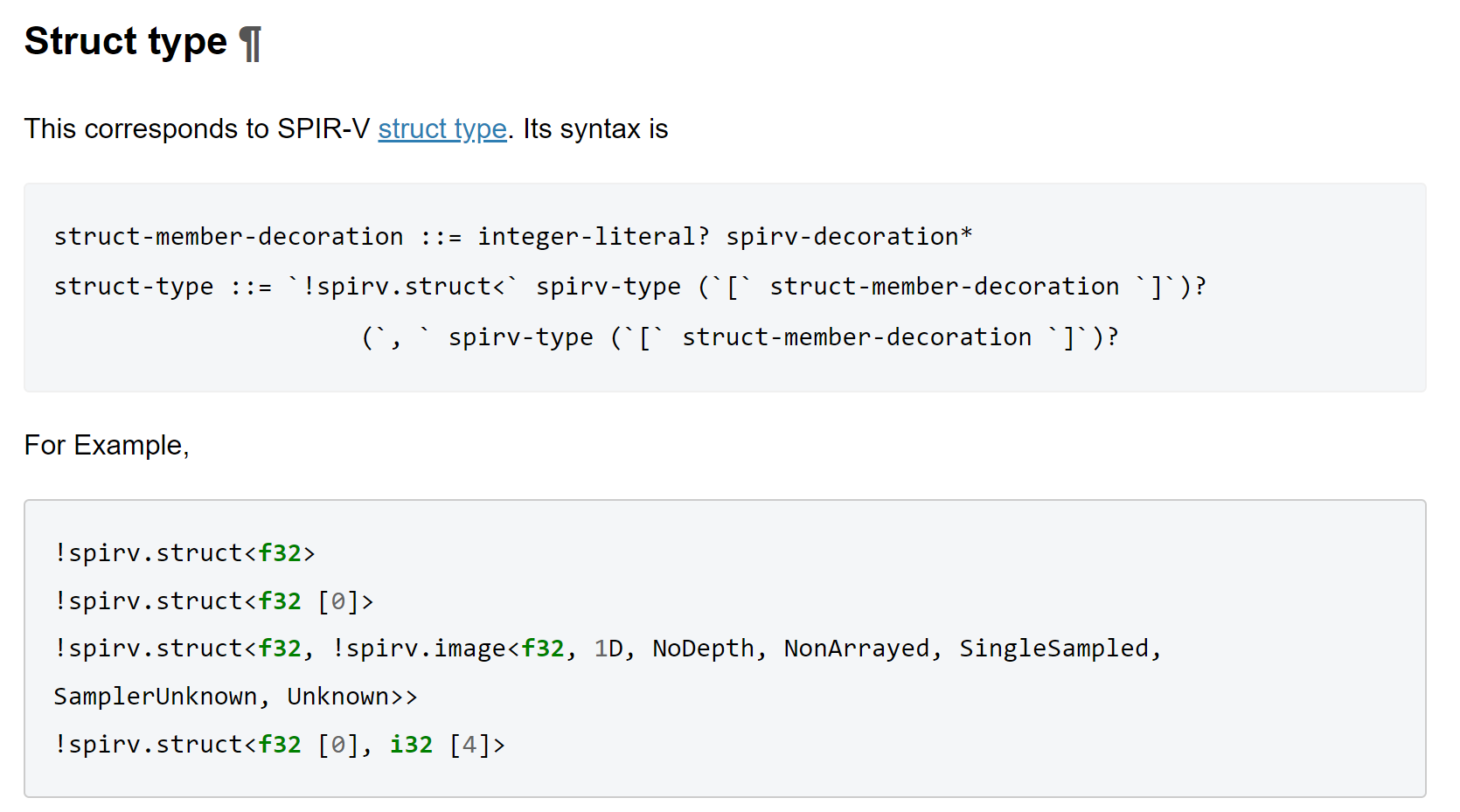 If I'm not mistaken, there should be a right bracket here? Signed-off-by: MingZhu Yan <[email protected]>
GETUID and GETGID are non-standard intrinsics supported by a number of other Fortran compilers. On supported platforms these intrinsics simply call the POSIX getuid() and getgid() functions and return the result. The only platform we support that does not have these is Windows. Windows does not have the same concept of UIDs and GIDs, so on Windows we issue a warning indicating this and return 1 from both functions. Co-authored-by: Yi Wu <[email protected]> --------- Co-authored-by: Yi Wu <[email protected]>
…lvm#110109) Change GlobalISelEmitter to use const RecordKeeper. This is a part of effort to have better const correctness in TableGen backends: https://discourse.llvm.org/t/psa-planned-changes-to-tablegen-getallderiveddefinitions-api-potential-downstream-breakages/81089
…pe ScalarTy. (llvm#110073) BoUpSLP::gather always use CreateInsertVector for FixedVectorType ScalarTy.
…#110472) Updates the return type of `getNumDynamicDims` and `getNumScalableDims` from `int64_t` to `size_t`. This is for consistency with other helpers/methods that return "size" and to reduce the number of `static_cast`s in various places.
Allocating wwm-registers and per-thread VGPR operands together imposes many challenges in the way the registers are reused during allocation. There are times when regalloc reuses the registers of regular VGPRs operations for wwm-operations in a small range leading to unwantedly clobbering their inactive lanes causing correctness issues that are hard to trace. This patch splits the VGPR allocation pipeline further to allocate wwm-registers first and the regular VGPR operands in a separate pipeline. The splitting would ensure that the physical registers used for wwm allocations won't take part in the next allocation pipeline to avoid any such clobbering.
The options are not translated correctly when targeting Vulkan using the dxc driver mode. Resuing the translator used for HLSL. Fixes problem 2 in llvm#108567.
…10125) Move static functions `Function::lookupIntrinsicID` and `Function::isTargetIntrinsic` to Intrinsic namespace.
GeneratedRTChecks::getCost duplicates getSmallBestKnownTC partially, when attempting to get the best trip-count estimate. Since the intent of this code is to get the best trip-count estimate, and getSmallBestKnownTC is written for exactly this purpose, replace the partial code-duplication with a call to this function.
After pr96656.ll were added to LAA and LoopVersioning, it was decided that the bug is in a caller of LoopVersioning, not in LAA or LoopVersioning itself. The new candidate was LoopLoadElim, but llvm#96656 has since been marked invalid. Hence, re-organize the added tests to avoid confusion, and the testcase from the investigation to LoopLoadElim.
Add noalias, where applicable, to eliminate unnecessary memory check, and regen with UTC.
These now get the default promote-to-float behavior, like half does. Fixes llvm#92899
 krzysz00
left a comment
krzysz00
left a comment
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I'm liking this idea.
This should also let me remove amdgpu.lds_barrier, perhaps - or at least lower to it.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Nit (assuming you're planning to upstream this): this is usually class inheritance (Args<>) or at the top of the block
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Thanks for your help! Glad you can also get something out of it.
Yes, the intention is to upstream.
It seems in checkOpenMPIterationSpace `OrderedLoopCountExpr` can also be null, so check before dereferencing.
112370f to
874dd36
Compare
…ext is not fully initialized (llvm#110481) As this comment around target initialization implies: ``` // This can be NULL if we don't know anything about the architecture or if // the target for an architecture isn't enabled in the llvm/clang that we // built ``` There are cases where we might fail to call `InitBuiltinTypes` when creating the backing `ASTContext` for a `TypeSystemClang`. If that happens, the builtins `QualType`s, e.g., `VoidPtrTy`/`IntTy`/etc., are not initialized and dereferencing them as we do in `GetBuiltinTypeForEncodingAndBitSize` (and other places) will lead to nullptr-dereferences. Example backtrace: ``` (lldb) run Assertion failed: (!isNull() && "Cannot retrieve a NULL type pointer"), function getCommonPtr, file Type.h, line 958. Process 2680 stopped * thread llvm#15, name = '<lldb.process.internal-state(pid=2712)>', stop reason = hit program assert frame #4: 0x000000010cdf3cdc liblldb.20.0.0git.dylib`DWARFASTParserClang::ExtractIntFromFormValue(lldb_private::CompilerType const&, lldb_private::plugin::dwarf::DWARFFormValue const&) const (.cold.1) + liblldb.20.0.0git.dylib`DWARFASTParserClang::ParseObjCMethod(lldb_private::ObjCLanguage::MethodName const&, lldb_private::plugin::dwarf::DWARFDIE const&, lldb_private::CompilerType, ParsedDWARFTypeAttributes , bool) (.cold.1): -> 0x10cdf3cdc <+0>: stp x29, x30, [sp, #-0x10]! 0x10cdf3ce0 <+4>: mov x29, sp 0x10cdf3ce4 <+8>: adrp x0, 545 0x10cdf3ce8 <+12>: add x0, x0, #0xa25 ; "ParseObjCMethod" Target 0: (lldb) stopped. (lldb) bt * thread llvm#15, name = '<lldb.process.internal-state(pid=2712)>', stop reason = hit program assert frame #0: 0x0000000180d08600 libsystem_kernel.dylib`__pthread_kill + 8 frame #1: 0x0000000180d40f50 libsystem_pthread.dylib`pthread_kill + 288 frame #2: 0x0000000180c4d908 libsystem_c.dylib`abort + 128 frame #3: 0x0000000180c4cc1c libsystem_c.dylib`__assert_rtn + 284 * frame #4: 0x000000010cdf3cdc liblldb.20.0.0git.dylib`DWARFASTParserClang::ExtractIntFromFormValue(lldb_private::CompilerType const&, lldb_private::plugin::dwarf::DWARFFormValue const&) const (.cold.1) + frame llvm#5: 0x0000000109d30acc liblldb.20.0.0git.dylib`lldb_private::TypeSystemClang::GetBuiltinTypeForEncodingAndBitSize(lldb::Encoding, unsigned long) + 1188 frame llvm#6: 0x0000000109aaaed4 liblldb.20.0.0git.dylib`DynamicLoaderMacOS::NotifyBreakpointHit(void*, lldb_private::StoppointCallbackContext*, unsigned long long, unsigned long long) + 384 ``` This patch adds a one-time user-visible warning for when we fail to initialize the AST to indicate that initialization went wrong for the given target. Additionally, we add checks for whether one of the `ASTContext` `QualType`s is invalid before dereferencing any builtin types. The warning would look as follows: ``` (lldb) target create "a.out" Current executable set to 'a.out' (arm64). (lldb) b main warning: Failed to initialize builtin ASTContext types for target 'some-unknown-triple'. Printing variables may behave unexpectedly. Breakpoint 1: where = a.out`main + 8 at stepping.cpp:5:14, address = 0x0000000100003f90 ``` rdar://134869779
This is to add an attribute to the gpu.barrier op to specify which level of memory to synchronize.